
How serious are ACL injuries?Īn ACL tear is a serious injury that can end an athlete’s season. With focused training, any athlete can increase the stability of their knees and reduce their risk of ACL injury. Girls often let their knees drop inward during maneuvers that involve cutting, pivoting, or landing, which can put more stress on the ligaments in their knees.Girls tend to land with straighter knees than boys, which reduces the effectiveness of their muscles as shock absorbers.This imbalance puts stress on their knees. Girls tend to have more strength in the muscles in the front of their thighs (quadriceps) than in the muscles in the back of their thighs (hamstrings).Unless they target their calves as part of their training, girls don’t tend to develop as much lower leg strength as boys as they grow.There are several possible reasons that ACL injuries affect more girls than boys: Girls are five to eight times more likely to tear an ACL than boys. Teenage athletes have the highest rate of ACL injuries, largely because they are the most physically active age group. This is why ACL tears are common in contact sports Contact and collisions: The ACL is at risk when an athlete’s knee is hit by or collides with another player or object.This includes sports like volleyball, basketball, figure skating, and gymnastics. Jumping and landing: In any activity that involves jumping, a hard or awkward landing can damage the ACL.Slowing down or stopping suddenly: Sprinting, then slowing down or coming to a complete stop can put a twisting force (torque) on the knee.Changing direction rapidly: A rapid turn or “cut,” common games like soccer, football, field hockey, lacrosse, and rugby, can put extreme pressure on the ACL and other ligaments in the knee.Athletic moves that strain the knee include: swelling around the knee within 24 hoursĪCL injuries typically happen while playing sports.knee pain so severe you can’t continue playing.sudden instability and feeling that the knee cannot support your weight.If you have injured your ACL, you probably heard a popping noise at the moment the ligament was sprained or torn.

Without these wedge-shaped pieces of cartilage, the thigh bone and shin bone would rub painfully against each other. The meniscus provides padding and shock absorption for the knee. These ligaments prevent the knee from bending too far to either side of the leg. Two other ligaments run along either side of the knee, the medial collateral ligament (MCL) and lateral collateral ligament (LCL). These ligaments prevent the shin bone from sliding too far forward or backward under the thigh bone. The ACL and another ligament called the posterior cruciate ligament (PCL) run through the center of the knee. The kneecap (patella) located in the front of the knee, protects the ACL and other knee ligaments. Where is the ACL located in the anatomy of the knee? The ACL is one of four main ligaments in the knee that attach the thigh bone (femur) to the shin bone (tibia). Proper athletic technique, such as positioning and landing with bent knees, can also reduce your risk. You can reduce your risk of an ACL injury or re-injury by developing your overall fitness, especially leg strength and balance.

The injury increases the risk of osteoarthritis in early adulthood. Patients who have torn an ACL are at high risk of repeat injury.
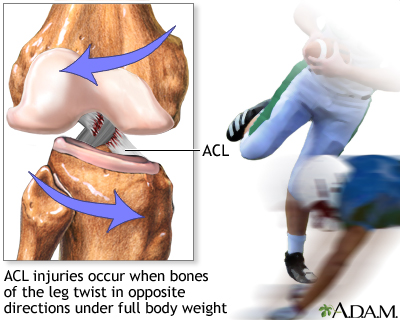
The type of surgical procedure depends on the patient’s age and their stage of growth. Usually, surgery is recommended to repair the knee. This often happens in combination with other injuries, such as a torn meniscus. The most common type of ACL injury in children is a complete ACL tear.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
